Would a dentist notice mouth cancer? And if they did, how can that be beneficial?
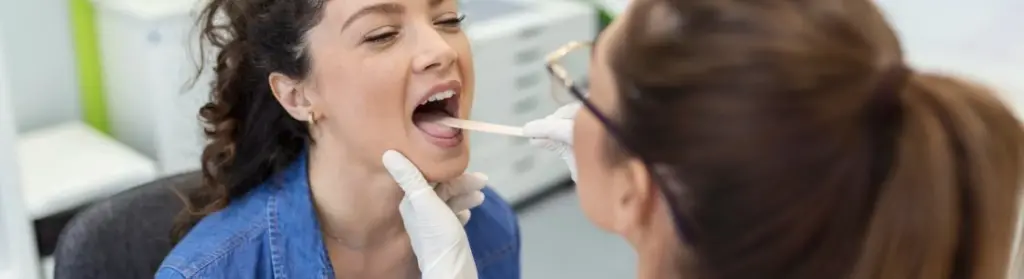
The answer is Yes. A dentist can notice mouth cancer. They often play a crucial role in detecting mouth cancer as they have specialized training and expertise in examining the oral cavity during routine dental check-ups.
How Dentists Can Detect Mouth Cancer During Routine Check-ups
The key to answering the question, “Would a dentist notice mouth cancer?” lies in examining the dentists role as far as routine check-ups are concerned, and how these checkups can help in mouth cancer detection..
Regular dental check-ups are an essential part of maintaining oral health, but they also play a significant role in detecting mouth cancer. Experienced dentists are trained to identify early signs and symptoms of oral cancer during routine examinations, enabling timely referrals for further evaluation and treatment.
During routine check-ups, dentists thoroughly inspect the oral cavity for any abnormalities that could be indicative of mouth cancer. Here’s how dentists detect potential signs of mouth cancer:
- Visual Examination: Dentists use proper lighting and magnifying instruments to visualize the lips, tongue, inner cheek surfaces, roof and floor of the mouth, gums, and throat area.
- Suspicious Lesions: Dentists monitor for suspicious lesions like red or white patches (erythroplakia/leukoplakia), ulcers that don’t heal within two weeks while ruling out other benign conditions like canker sores or aphthous ulcers.
- Lumps or Bumps: Any unusual lumps/bumps may require further investigation as these could potentially indicate tumor growth.
- Unexplained Bleeding/Numbness: Dentists look out for any unprovoked bleeding from the oral tissues or persistent areas of numbness/tingling on the lip/tongue/cheek which might signal nerve involvement due to malignancy.
- Digital Imaging: A Houston holistic dental specialist may employ intraoral cameras or handheld devices capable of capturing high-resolution images to record a detailed visual representation of all oral structures that can be stored electronically for future comparisons.
- Progress Analysis: By comparing digital imaging records over time with current observations during subsequent visits/dental check-ups, any changes in appearance (growth/spread) can be identified promptly.
- Palpation Examination: In addition to visual examination, dentists use palpation techniques by gently feeling the lymph nodes on the neck/jawline and assessing oral tissues (lips/cheeks) for any abnormalities.
- Lymph Node Abnormalities: Palpating lymph nodes provides information regarding their size, consistency changes (enlarged/firm/matted), which could imply spread of cancer cells from primary tumor site within the mouth.
- Patient History Assessment: Dentists take detailed patient histories, asking questions about risk factors and specific symptoms associated with mouth cancer.
- Smoking/Tobacco Usage: Dentists will inquire about smoking habits including cigarettes/cigars/pipes/chewing tobacco as these are strongly correlated with increased mouth cancer risks.
- Alcohol Consumption: Assessing alcohol intake patterns is crucial as excessive consumption raises oral cancer susceptibility independently or when combined with tobacco usage.
- Family Cancer History: Inquiring about familial incidents of cancers can aid in evaluating genetic predispositions for developing malignancies.
- Referral for Specialist Evaluation: If a dentist observes any suspicious lesions, or growths or detects abnormalities during routine examinations, they may refer patients to oncology specialists for further evaluation and diagnosis.
Screening Tests and Tools Used by Dentists to Identify Mouth Cancer
If the answer to the question, “Would a dentist notice mouth cancer?” is a resounding yes, then it is natural to wonder how exactly they would be able to do it.
Screening for mouth cancer involves using various tests and tools to identify potential signs of malignancy during routine dental visits. These screening methods help dentists detect oral abnormalities early on so that appropriate referrals can be made promptly.
Here are some screening tests and tools used by dentists to identify mouth cancer:
- Visual Inspection: Dentists conduct a thorough visual examination of the oral cavity using proper lighting, magnifying instruments, and handheld mirrors.
- Lip and Facial Examination: Dentists look for any abnormalities like crusts/cracks/red or white patches/swellings on the lips or facial areas exposed to sunlight.
- Intraoral Examination: This involves observing the tongue, inner cheek surfaces, gums, roof/floor of the mouth, and throat area looking for any suspicious lesions like ulcers that do not heal within two weeks.
- Tactile Examination (Palpation): Dentists gently feel around the neck/jawline areas to evaluate lymph nodes for size/consistency anomalies (enlargement/firmness).
- Digital Imaging Techniques: Dentists use intraoral cameras or handheld devices capable of capturing detailed images. Digital imaging helps document current visual representations of oral structures and enables comparisons over time during subsequent visits.
- Tissue Biopsy: If suspicious lesions or growths are found during routine examinations, dentists may perform a biopsy procedure where small tissue samples are taken from abnormal areas using specialized instruments such as punch biopsies or scalpel incisions.
- Diagnostic Analysis: These tissue samples are sent to laboratories where pathologists examine them under a microscope to determine if malignancy is present.
- Oral Brush Biopsy (cytology brush): An alternative method sometimes employed in preliminary screenings involves taking a sample from suspicious areas such as red/white patches by scraping with an oral cytology brush followed by microscopic analysis of collected cells, looking for malignant changes/typical cellular abnormalities.
- Fluorescence-based Screening Systems: Some dentists utilize advanced fluorescent light technology systems that highlight cell nuclei variations in differentiating normal tissues from potentially precancerous/malignant ones while examining the oral tissues.
- Tissue Autofluorescence: The excitation of oral tissues by specific wavelengths of light causes normal cells to emit a characteristic fluorescence pattern, whereas abnormal/precancerous/malignant cells exhibit altered fluorescence patterns due to underlying pathological changes.
- Enhanced Visual Contrast Examination: Fluorescent visualization aids in distinguishing suspicious areas that may be missed under routine white light examination alone helping in mapping for potential biopsy sites.
- Toluidine Blue Staining: A dye called toluidine blue is sometimes used during an examination where it selectively stains abnormal cells. Dentists observe if any stained areas retain coloration longer than surrounding normal tissue while also considering other clinical factors that lead to further evaluation steps.
It’s important to remember that while these screening tests and tools assist in identifying potential signs of mouth cancer, they cannot provide a definitive diagnosis on their own. Diagnostic confirmation relies on the laboratory analysis of biopsied tissues or cell samples collected through the procedures mentioned above.
Early Detection Strategies for Preventing Advanced Stages of Mouth Cancer
While it is true that the answer to the question, “Would a dentist notice mouth cancer?”, is that they can actually do so, this does not mean that it is all on them. You too can help to ensure that your mouth cancer is detection as early as possible.
Early detection plays a pivotal role in preventing advanced stages of mouth cancer. Also, early detection improves treatment outcome rates. Regular oral health check-ups combined with awareness about risk factors and self-examination techniques can help individuals identify potential signs at an early stage
Here are some strategies for early detection:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule routine dental visits at least once every six months or as recommended by your dentist. This includes scheduling for Houston holistic oral cancer screenings. These visits allow dentists to thoroughly examine the oral cavity for any abnormalities during visual inspections and physical examinations.
- Dentist Expertise: Experienced dentists can recognize subtle changes indicative of pre-cancerous or cancerous conditions that might otherwise go unnoticed by individuals themselves.
- Oral Cancer Screenings: Dentists may perform additional screening tests or use specialized tools to examine the oral tissues for potential abnormalities, enabling early detection and timely referrals if necessary.
- Self-Examination: Conduct regular self-examination at home to familiarize yourself with your oral structures and monitor any changes over time.
- Mirror Observations: Use a well-lit mirror to visually inspect the lips, tongue, inner cheek surfaces, gums, roof/floor of the mouth for any suspicious lesions (ulcers/red/white patches), lumps/bumps/swellings that don’t resolve within two weeks.
- Palpation Techniques: Gently feel around your neck/jawline area to assess lymph nodes for enlargement or consistency changes.
- Be Mindful of Risk Factors: Understand common risk factors associated with mouth cancer and identify if any apply to you personally. Awareness can help in adopting preventive measures or seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms arise.
- Self-Awareness of Symptoms: Learn about the signs and symptoms related to mouth cancer so that you can recognize them early on.
- Persistent Sores/Ulcers: Inspect the inside of your mouth regularly for persistent sores/ulcers that do not heal within two weeks or tend to recur frequently.
- Changes in Oral Tissues: Pay attention to any changes in color (red/white patches) or texture (thickenings/lumps) on soft tissues inside the mouth.
- Difficulty Swallowing/Talking/Eating/Pain: Note if you experience unexplained pain while chewing/swallowing, difficulty speaking/eating due to movements restrictions/mouth opening limitations
- Avoid High-Risk Behaviors/Factors:
- Smoking/Tobacco Usage Cessation: Quitting smoking/chewing tobacco significantly reduces your chances of developing oral cancers as it removes a significant risk factor.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderation in alcohol consumption or abstaining altogether helps minimize mouth cancer risks and synergistic effects with tobacco usage if you do smoke or chew.
- Sun Protection: Apply UV-blocking lip balms, wear hats when exposed to direct sunlight for prolonged periods, especially during peak hours between 10 am – 4 pm.
- Oral Health Practices: Maintaining good oral hygiene by regular brushing, flossing, using mouthwashes alongside professional dental cleanings helps reduce inflammation/gum diseases that might contribute cellular stress leading to carcinoma transformation possibilities.
- Dental Appointments: Promptly address any dental health concerns such as chronic gum/periodontal diseases/infections that may increase the likelihood of malignant transformations over time when left untreated.
- Educating Others and Creating Awareness: Share your knowledge about mouth cancer risks, early detection strategies and screening practices with friends, family members or community groups to encourage preventive measures and timely screenings.
It’s important to remember that even with proactive efforts for early detection and prevention, some individuals may still develop mouth cancer. However, early diagnosis by a Houston holistic dentist significantly improves treatment outcome rates by facilitating prompt intervention before the disease progresses to advanced stages.
Collaborative Efforts Between Dentists and Oncologists in Managing Oral Cancers
When answering the question, “Would a dentist notice mouth cancer?”, it is also important to appreciate the role that dentists play after they suspect mouth cancer. As a result, examining their collaboration with other experts is important when discussing this question.
Collaboration between dentists and oncologists is essential in managing oral cancers effectively. Both professionals play distinct yet interconnected roles during various stages of diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up care for patients with oral malignancies.
Here are the collaborative efforts between dentists and oncologists:
- Early Detection: Dentists detect initial signs or suspicious abnormalities during routine dental examinations that can be indicative of oral cancers.
- Referrals: By promptly referring patients to oncology specialists for further evaluation/biopsy procedures, dentists contribute to early detection and timely management.
- Diagnostic Confirmation: After referrals, oncologists carry out additional tests like tissue biopsies/laboratory analysis to definitively diagnose mouth cancer.
- Collaboration: Dentist-oncologist collaboration involves exchanging patient information/dental records facilitating accurate diagnoses; sharing biopsy results supporting interdisciplinary understanding regarding medical imaging findings if required for comprehensive assessment/productive team input prior building custom treatment plans accommodating one’s individual needs appropriately
- Treatment Planning:
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Dentists collaborate with radiologists/pathologists/oncological surgeons/radiotherapists concerning proposed treatment action steps developing an effective customized plan while utilizing their united specialized knowledge blending surgical skills with oral health preservation during treatments when possible (e.g., dental screenings prior to radiation therapy).
- Oral Health Assessment: Dentists perform comprehensive dental evaluations to identify any potential oral health issues that may affect cancer treatment outcomes, such as tooth decay, gum disease, or infections. They work closely with oncologists to ensure optimal oral health before and during treatment.
- Supportive Care Management:
- Managing Side Effects: Oncologists and dentists collaborate in managing common side effects of cancer treatments, such as mucositis (inflammation of the mouth), dry mouth, taste changes, and oral infections.
- Preventive Measures: Dentists provide supportive care measures like prescribing special mouth rinses/gels for oral pain relief; altering dietary suggestions (soft/moist/tolerable foods) while considering necessary precautions conforming to specific patient needs.
- Dental Rehabilitation: Post-treatment, dentists work alongside oncologists providing rehabilitative dental procedures/reconstruction ensuring optimal restoration of lost functional aspects/maintaining aesthetics where appropriate.
- Follow-up Monitoring:
- Oral Examinations: Regular follow-up appointments involve dentists conducting visual/oral examinations monitoring recurrent/cancer-free status while addressing any concerns that may arise post-treatment.
- Shared Communication/Referrals: Collaboration includes ongoing communication sharing progress updates regarding patients’ statuses/pathology findings facilitating cautious referrals based on advancements in management necessities throughout survivorship journeys.
Collaborative efforts between dentists and oncologists are vital for achieving successful outcomes in the diagnosis, treatment planning, and long-term management of patients with oral cancers. Their coordinated approach ensures comprehensive care while preserving optimal oral health and quality of life for individuals affected by this disease.
Final Thoughts on the Question: Would a Dentist Notice Mouth Cancer
In conclusion, dentists play a crucial role in detecting mouth cancer early on. However, they’re not able to diagnose it definitively based on visual examinations alone. But their expertise allows them to recognize suspicious lesions promptly and initiate appropriate referral pathways for accurate diagnosis and timely management by specialists.
Regular dental check-ups are vital because early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes for oral cancers. Therefore, it is important not to underestimate the value of routine dental visits in detecting potential signs of mouth cancer.